Finishing and Bindery Services
In printing, finishing refers to value-added operations that are performed after the printing has been completed. Some finishing operations can occur before the printing comes off the press (inline), but many finishing operations are performed after the printing comes off the press (offline).
Many printers have a Finishing/Bindery department, which performs a wide variety of services to enhance the function and appearance of printed pieces. Most of the more popular Finishing and Bindery services we offer are listed here:
Click on any image below to see a larger picture.
Types of binding:
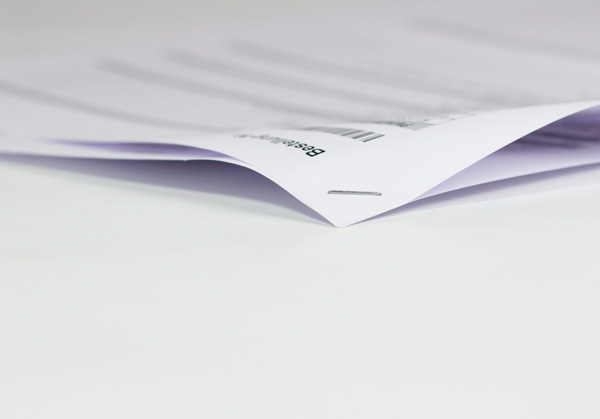
Binding is a broad term used to describe the gathering and fastening together of separate sheets or signatures. Binding can be as simple as placing a single staple through the corner of a set of documents. However, binding usually refers to the creation of durable books and booklets. Examples of popular binding methods include perfect binding, saddle-stitching, spiral/coil binding, as well as the insertion of components into a ringed binder. Spiral/Coil Binding
Spiral/Coil BindingWhen pages are fastened together by a spiral of wire or plastic that coils through a series of holes punched along one side of each page and the front and back covers. Black plastic coil-binding is standard at Printing Services, but other colors are available.
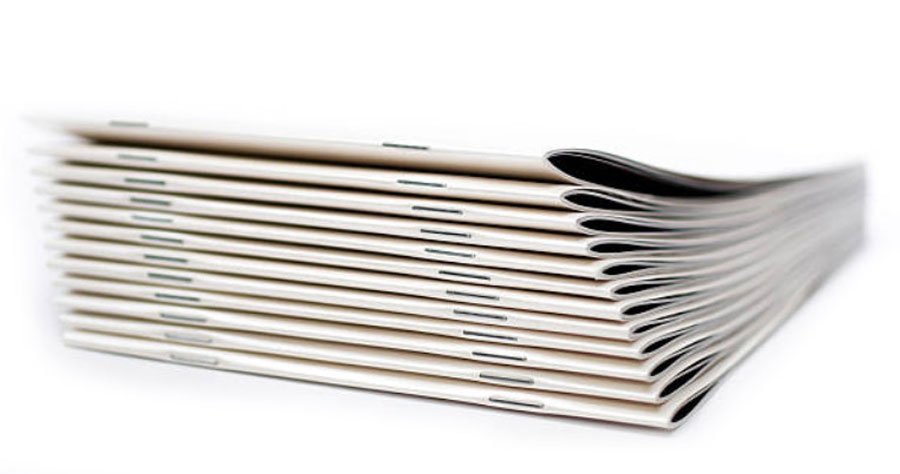 Saddle-Stitching
Saddle-StitchingThe method in which folded sheets are gathered together one inside the other and then stapled through the fold line with wire staples. The staples pass through the folded crease from the outside and are clinched between the centermost pages. Two staples are commonly used but larger books may require more staples along the spine.
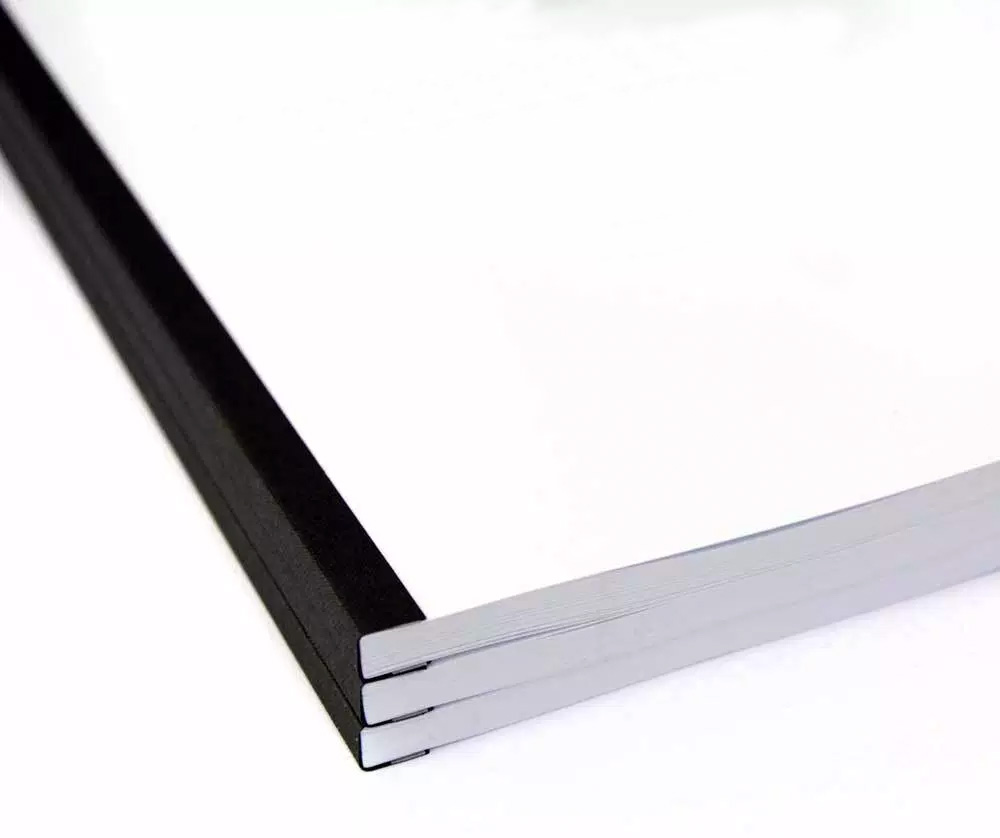
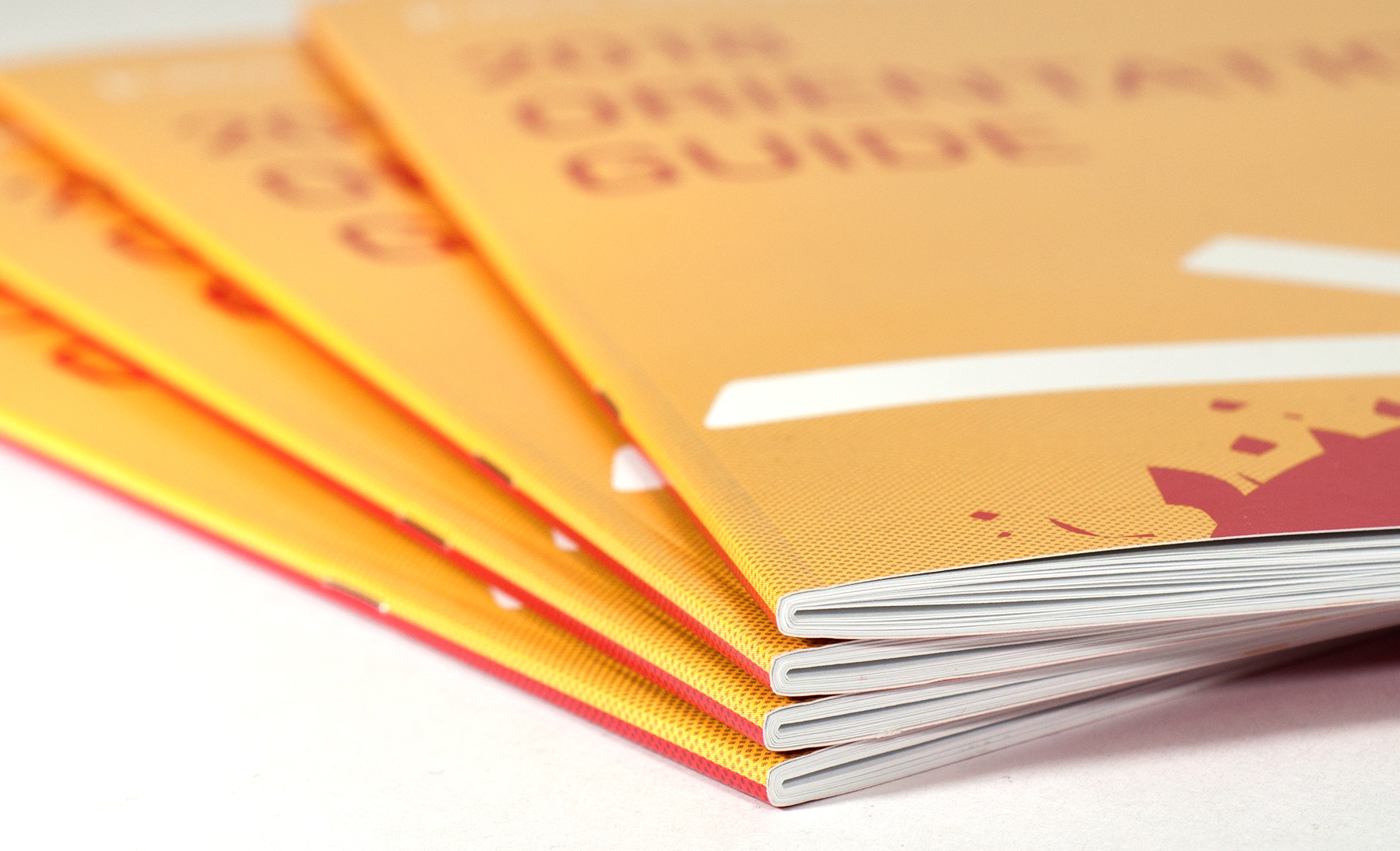
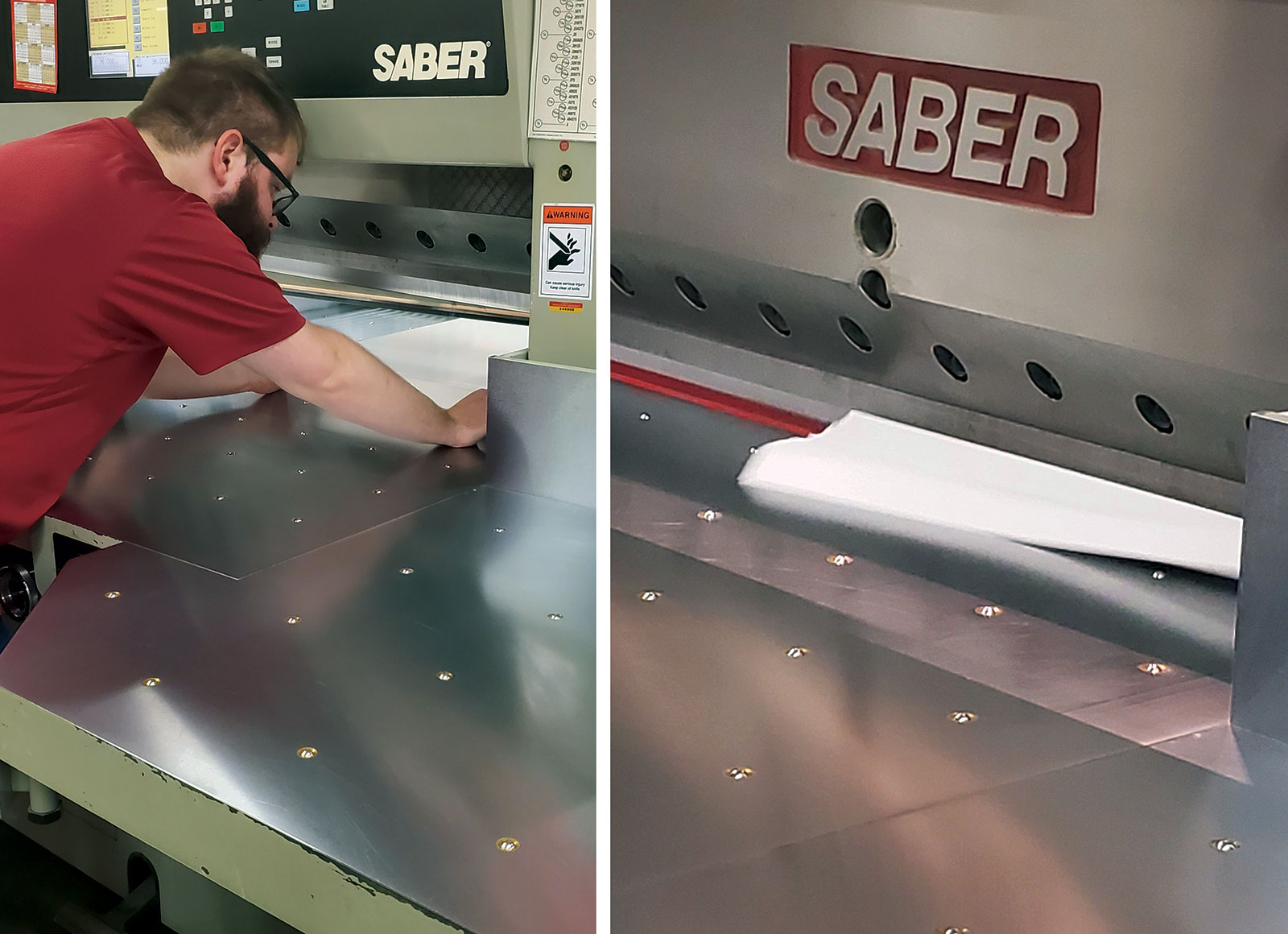
Cutting and TrimmingUsing a blade to reduce a printed piece down to its desired size. Common examples include removing excess paper along crop marks, separating pieces that have been printed as multiple images per sheet, or trimming the open edges of a book to create evenly aligned pages. |
|||||||||||
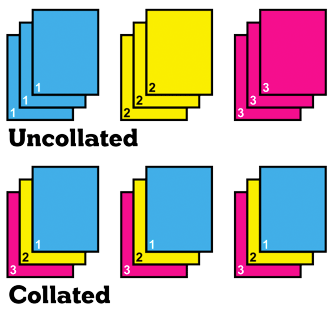
CollatingThe gathering and arranging of individual sheets or other printed components into a predetermined sequence. Collating creates consistent, logical sets. |
|||||||||||
Scoring and CreasingThe process of making a score or crease in paper so it will fold easier. Used mostly on heavyweight papers and cardstock.
|
|||||||||||
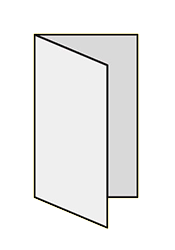
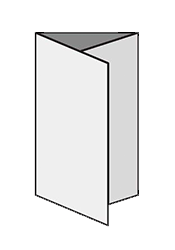
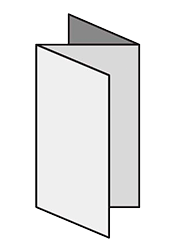
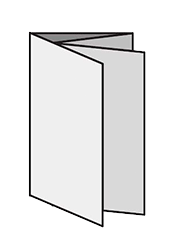
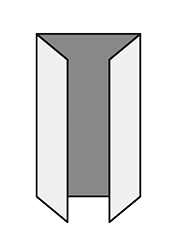
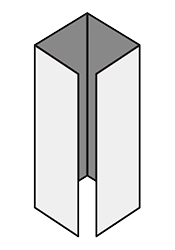
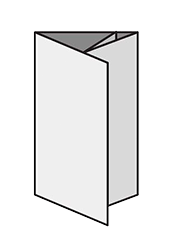
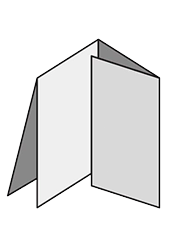
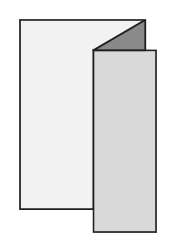
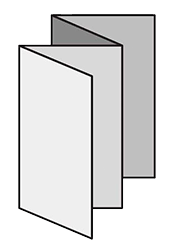
FoldingA procedure that bends over a printed piece so that it lies flat upon itself. Folding serves many functions, one of which is to reduce the physical size of a printed piece. This allows the piece to fit into something else – like an envelope, packaging, or display rack. A smaller size can also make certain printed items easier to handle and/or distribute. Folding is also commonly used as a design technique to create separate panels from a single sheet, such as for a brochure or invitation.There are numerous folding styles available:
|
|||||||||||
LaminatingImproving durability, the process of bonding a clear plastic film onto printed matter to protect against stains, smudges, moisture, wrinkles, and tears. Lamination is a popular choice for printed items that must endure heavy use and/or outdoor elements. This can apply to both small and large format-printing.
|
|||||||||||
OverlaminateApplying a thin adhesive film layer, on one side, to protect a graphic, often with anti-UV properties. It can also add aesthetic qualities, such as adding a gloss, matte, textured or even a dry-erase-receptive finish to the final product. This method is most commonly used for outdoor wide-format signage and graphics, where one side of piece has adhesive. |
|||||||||||
Die-CuttingIn the world of printing, a Die refers to a thin, razor-sharp steel blade that has been formed into a specific shape or pattern (sort of like a heavy-duty cookie-cutter). Consequently, Die-Cutting refers to the act of using this sharp die to cut paper, cardstock, label-stock, or other substrates into various (static/same) shapes.Contour-CuttingCutting to a specific shape by using a digital cutter or router, which creates a precise cut along the edge of a design/graphic. This process allows for variable sizes and shapes, where die-cutting is limited to being static/same.Kiss-CuttingThe process of only cutting through the first layer of a printed material (typically vinyl), while the backing (typically a paper liner) stays intact. This can be done with both Contour-Cutting and Die-Cutting. This is common when printing and cutting stickers and labels. |
|||||||||||
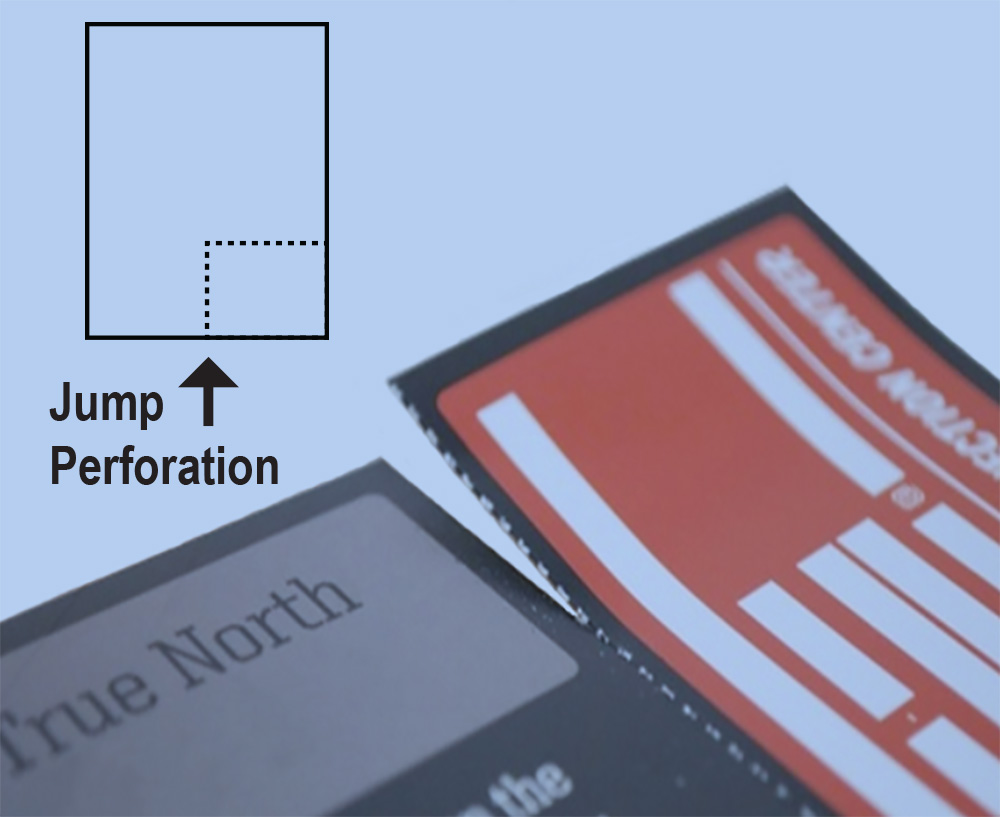
PerforatingA procedure that creates a series of very fine holes in paper or cardstock, usually along a straight line, to allow a portion of the printed piece to be easily detached by hand. Used for a variety of purposes, such as coupons, ID cards, response cards, and remittance slips. Jump/Partial Perforation: when the perforation does NOT extend across the entire sheet. (this may be common with postcard tear-outs on the back of a brochure) |
|||||||||||
UV-CoatingA clear-coat applied over printed materials to improve resilience and appearance. This coating is applied in liquid form, then exposed to ultra-violet light which bonds and dries it instantly. Multiple finishes are available, with the most common being gloss and matte. |
|||||||||||
Drilling/PunchingRefers to the process of creating holes in paper using a rotating bit or die-punch, such as the hole patterns needed for sheets and dividers placed into ringed binders, or for coil-binding. |
|||||||||||
Embossing / DebossingRefers to the method of pressing an image into paper or cardstock to create a three dimensional design. Embossing results in a raised surface; debossing results in a depressed surface. (special order) |
|||||||||||
Foil StampingA specialized process that uses heat and pressure to apply a metallic foil design to a printed piece. The foil is usually a gold, silver, or copper tone, though a variety of colors are available. Foil stamping adds elegance and distinction and can be combined with the embossing technique to create a metallic design in relief. (special order) |
|||||||||||
PaddingApplying a flexible adhesive along one edge of a stack of same-sized sheets. The adhesive secures the sheets as a unit, but allows the topmost sheet to be easily removed as needed. In most cases, padded sheets incorporate a chipboard backer for rigidity. Common examples include notepads, memo pads, and order pads. |
|||||||||||
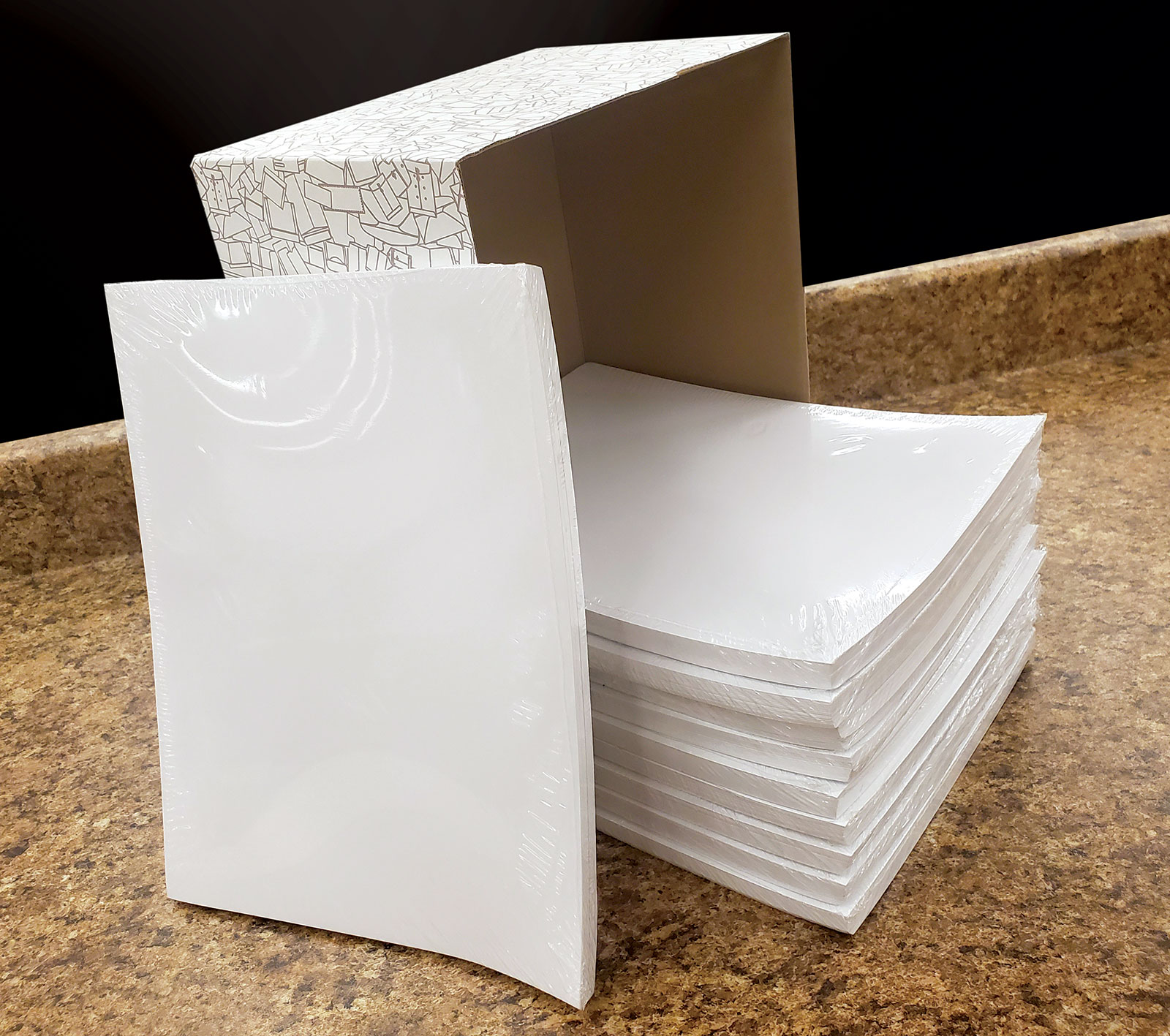
Shrink-WrappingA packaging method that encloses bundles of printed matter within a transparent plastic film. The application of heat makes the film shrink around the printing to secure it tightly. In addition to providing a layer of protection, shrinkwrapping is a cost-effective way to create convenient-sized packs, allowing for easier handling and distribution of the printed pieces. |
|||||||||||